On this page:
✔️ Motivation
✔️ Background Info
✔️ Your Task
✔️ Requirements
✔️ Handing in
✔️ Grade Breakdown
Motivation (Why are we doing this?)
This lab will help you solidify your understanding of self-balancing trees, in particular heaps. You’ll also implement heapsort as a part of this lab.
Background Info
Heaps
Heaps are special implementations of Complete Binary Treess and come in two flavors: Min-Heap and Max-Heap.

The difference between these structures are their special rules:
- Min-Heap: The key at the root node must be the minimum among the keys present in its children.
- Max-Heap: The key at the root node must be the maximum among the keys present in its children.
Heap Operations
For most operations in a Heap, we need to envision each Node in a heap as being “indexed” (not literally indexed as an array is!) as so:
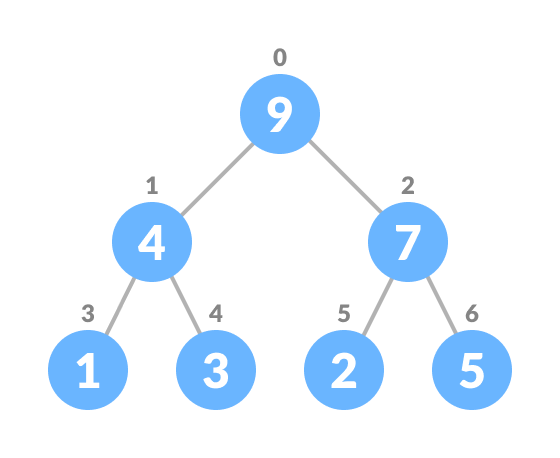
The root Node is index 0. We then we proceed left-right, top-down to “index” the remaining Nodes. Take a good look at the diagram above and make sure you understand it, as it will be necessary for your lab implementation below.
Your Task
Complete the implementation of a MIN heap. Pay attention to the hints in the code (CPP AND H FILES).
-
Download the files below (it’s easiest if you right click and then choose download or save)
- heap.h
- Contains the declaration of the lab you’ll be implementing. Do not alter any of the given function signatures.
- heap.cpp
- Contains the definition of the lab you’ll be implementing.
- test.cpp
- EMPTY TEST FILE (with a template for you to follow). You should add your own test cases to this file.
- doctest.h
- The library we’ll be using for our own automated tester. There’s a ton of code in here so don’t worry too much about understanding everything it does– just know the library is extremely powerful and we’ll only be scratching the surface of everything it can do. Do not edit this file.
- Once you have downloaded all the files, inspect them. Ask questions if you have them.
- Create your own makefile to compile and run your program. Refer to Lab 3 as needed.
- As you hopefully noticed, a lot of these functions are familiar. Use your Lab 20 implementation to complete the following functions:
heightpreorderinorderpostorderdestroyisFullisCompletesize
- Complete the implementation of
min_heapify. Pay attention to the comments and hints in the code. Refer to the course material (slides, readings, and background info above) as needed.- This is a MIN heap so all children must be larger than their parents
- Complete the implementation of
insert. Pay attention to the comments and hints in the code. Refer to the course material (slides, readings, and background info above) as needed.- This is a MIN heap so all children must be larger than their parents
- Add your own test cases for the functions you just completed. Run, compile, and test your program by running
makein your terminal, while in the directory all these files are located in. Debug as needed. - Complete the implementation of
find_last. Pay attention to the comments and hints in the code. Refer to the course material (slides, readings, and background info above) as needed. - Add your own test cases for the function you just completed. Run, compile, and test your program by running
makein your terminal, while in the directory all these files are located in. Debug as needed. - Complete the implementation of
remove_min. Pay attention to the comments and hints in the code. Refer to the course material (slides, readings, and background info above) as needed. - Add your own test cases for the function you just completed. Run, compile, and test your program by running
makein your terminal, while in the directory all these files are located in. Debug as needed. - Complete the implementation of
delete_element. Pay attention to the comments and hints in the code. Refer to the course material (slides, readings, and background info above) as needed. - Add your own test cases for the function you just completed. Run, compile, and test your program by running
makein your terminal, while in the directory all these files are located in. Debug as needed. - Complete the implementation of
search. Pay attention to the comments and hints in the code. Refer to the course material (slides, readings, and background info above) as needed.- HINT: This will look more like the search from Lab 19 than the one from Lab 20.
- Add your own test cases for the function you just completed. Run, compile, and test your program by running
makein your terminal, while in the directory all these files are located in. Debug as needed. - Add a public void function,
heapsort, to your H and CPP files. The function should take in an array of integers and an integer representing the size of the array. - Complete the implementation of
heapsort.- Build a heap from the numbers in the array passed in and then rewrite the contents of the array so they’re in sorted order
- Add your own test cases for the function you just completed. Run, compile, and test your program by running
makein your terminal, while in the directory all these files are located in. Debug as needed.
Requirements
Your goal for this lab is to complete the following tasks in order:
- All heap functions behave as expected for a min heap
- Heapsort function behaves as expected
Handing in
To submit your solution to Gradescope, select all of the following files and use the drag and drop option:
- heap.h
- heap.cpp
- test.cpp
Grade Breakdown
You must successfully meet requirement 1-2 in order to receive credit for this assignment.
To receive any credit at all, you must abide by our Collaboration and Academic Honesty Policy. Failure to do so may result in a failing grade in the class and/or further disciplinary action.
Original assignment by Christian Esteves, used and modified with permission.